Exploring the Hidden Life of Leptodactylodon ornatus: The Ornate African Forest Frog#
Deep within the shaded embrace of African rainforest streams lives a small yet charismatic creature rarely seen by human eyes: the Ornate African Forest Frog, scientifically known as Leptodactylodon ornatus. Much like an ancient secret quietly sustained by lush green foliage, moisture-laden air, and shadowy forest floor ambiance, this amphibian enchants and intrigues those lucky enough to discover its existence. Notoriously elusive, this delicate frog species serves as an ambassador to the astonishing biological richness and delicate ecological balance of Central Africa’s tropical rainforests.
With remarkable adaptations and unique behaviors, the Leptodactylodon ornatus isn’t merely another frog species—it’s a living emblem of the wonders hidden within Earth’s biodiversity hotspots. Its presence in the ecosystem tells tales of intricate ecological networks, environmental stability, and, perhaps alarmingly, reflects the ongoing state of habitat pressures and challenges faced by many hidden rainforest creatures.
Taxonomy and Classification#
The Ornate African Forest Frog, Leptodactylodon ornatus, belongs to the Amphibian class (Amphibia) and falls inside the Anuran order—frogs and toads known for their tailless morphological form. Within this order, it is housed under the Arthroleptidae family, particularly specialized frogs native to the sub-Saharan African forests.
The genus Leptodactylodon, meaning “slender-fingered tooth,” includes frogs characterized by their relatively diminutive size and subtle coloration adapted for camouflage. Closely related species within this genus also tend toward similar habitats—moist, humid montane rainforests beside pristine freshwater streams and rocky substrates.
Within the Arthroleptidae family, the Ornate African Forest Frog shares morphological and ecological traits with related amphibians like Astylosternus frogs. These similarities offer fascinating insights into the evolutionary paths that shape biodiversity within densely forested African habitats.
Natural Habitat#
No ecosystem encapsulates the vibrant, hidden, and often elusive world of amphibious life as vividly as the Central African rainforest. It is within this lush tapestry of life—rich in biodiversity and acclaimed for its abundance of unique fauna—that Leptodactylodon ornatus thrives.
Geographical Range and Distribution#
The distribution of Leptodactylodon ornatus spans across select regions within Cameroon and Nigeria, particularly thriving in montane forests along mountainous slopes, sometimes venturing into lower elevation habitats where microclimates remain consistently humid and shaded. Notably tied to pristine flowing freshwater streams coursing through heavily vegetated areas, their population is intricately wrapped in the stability and conservation of these fragile forest habitats.
Habitat Preferences#
Exploring the habitat of the Ornate African Frog reveals a marked preference for pristine montane and submontane forests, primarily around clear, oxygen-rich streams. These moisture-dependent creatures flourish among the damp leaf deritus, moss-covered rocks, and deep leaf-litter, perfectly camouflaged amidst the rainforest floor’s intricate patterns. They rely on this complex microhabitat for shelter, hunting grounds, and breeding sites, a reminder of how intimately a species can be linked to the health of its surrounding environment.
Their existence signifies ecological equilibrium—overly disturbed or altered landscapes simply cannot support their needs. Thus, encountering this frog inherently signals a relatively healthy, well-preserved forest ecosystem.
Physical Characteristics#
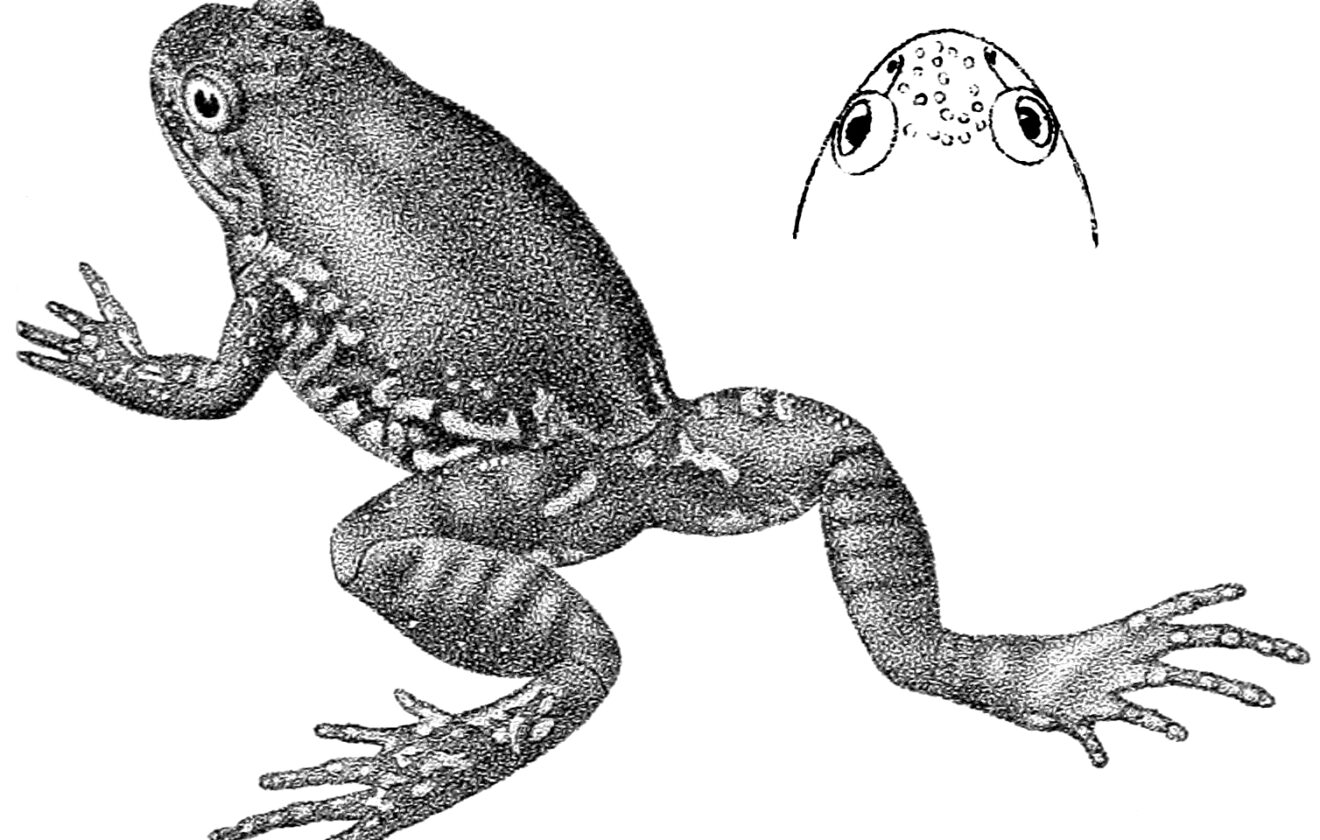
At first glance, the Ornate African Forest Frog seems unassuming and subtle. However, upon closer inspection, one quickly discerns its exquisite adaptations that render it perfectly suited to its habitat and lifestyle. Typically compact and petite in appearance, adults usually measure between 35 to 45 mm, fitting comfortably within the palm of a human hand.
Their muted coloration is a unique blend of browns, tans, greens, and occasionally flecks and streaks of darker pigments, an adaptation that proves invaluable for camouflage amidst the rainforest ground’s leaf-laden mosaic. This cryptic coloration helps the frogs evade predators by blending seamlessly into their surroundings, resembling fallen leaves or mottled rocks along streambeds.
Bearing slender, elongated digits suited for gripping damp, slippery rocks and vegetation, the frog’s limbs represent evolutionary craftsmanship attuned precisely to their watery and forest-floor habitats. Their eyes, relatively large and reflective, channel available ambient light beneath dense canopies, providing superior low-light vision capabilities crucial for nocturnal activity.
Behavior and Life Cycle#
Leptodactylodon ornatus exhibits patterns and behaviors barely perceptible to human observers yet strikingly well-adapted for survival within complex rainforest ecosystems. Primarily nocturnal, these frogs emerge from daytime refuges beneath damp leaves and rocky crevices with twilight’s beckoning.
Feeding Habits and Hunting Techniques#
When darkness descends, so begins their nightly ritual of hunting. Feeding primarily on insects, small arthropods, and forest floor invertebrates, they rely on keen senses and rapid reflexes rather than prolonged pursuits. With tongues rapid enough to evade human perception, bites occur in milliseconds—precisions perfected by millions of years of evolutionary fine-tuning.
Reproduction and Parental Care#
Amid the damp and shaded streamsides concealed beneath dense foliage, males can be heard emitting soft and discrete mating calls during rainy seasons to entice receptive females. After a brief but delicate courtship, egg-clusters are laid discreetly within shallow waters or carefully hidden on permanently moist surfaces.
Tadpoles, once hatched, develop in clear, oxygen-rich waters, distinctive by their particular mouthparts perfectly designed for scraping algae and microorganisms off surfaces—a striking adaptation for communal tadpole nurseries that exist in shallow pools and slow-moving waters along the streambeds.
It is within this softly flowing aquatic cradle that they gradually mature into froglets, developing lungs and limbs to prepare their transition to terrestrial life. Each stage in this transformation embodies the intricacies and marvels of a finely tuned amphibious lifecycle, reinforcing their deep reliance upon stable, diverse habitats for survival.
Ecological Role#
Though easily overlooked due to its size and concealed lifestyle, Leptodactylodon ornatus fulfills profound ecological responsibilities within its forest ecosystem. As active insectivores, they play pivotal roles in regulating insect populations, protecting plants from excess herbivory, and aiding in nutrient cycling by controlling detritivorous arthropods.
Simultaneously, they serve as essential prey for various small vertebrates: snakes, small mammals, birds, and larger amphibians. Thus, these frogs represent crucial ecological linchpins, ensuring balance on multiple trophic levels through their respective ecosystem roles.
Moreover, amphibians like Leptodactylodon ornatus are invaluable as bioindicators—species whose presence reflects an ecosystem’s overall health. Their notably sensitive skins rapidly absorb environmental contaminants, making them a non-negotiable indicator of environmental quality.
Threats and Conservation Status#
Regrettably, despite their subtle existence, the Ornate African Forest Frogs face mounting threats jeopardizing their populations and habitats. Habitat destruction through deforestation, logging practices, agriculture, and infrastructure development severely impact the sanctity of their environments. Coupled with the broader documented global declines in amphibians linked to climate change, pollution, and diseases like chytrid fungus, these little amphibians stand at significant ecological crossroads.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) categorizes Leptodactylodon ornatus as Vulnerable, signifying they face an elevated risk of extinction in the wild. Conservation initiatives emphasizing habitat conservation, research monitoring, and community education are critical interventions needed to restore and maintain viable populations.
Cultural and Scientific Significance#
Though rare attention has been paid historically to such discrete amphibians culturally, their scientific importance remains exceptional. Research involving such species contributes immensely to understanding broader ecological systems, climate pressures, and environmental disturbances’ impact upon amphibious life. By studying their behaviors, physiology, and population dynamics, researchers gain insights into ecological health management, conservation strategies, and potentially new biochemical compounds beneficial to scientific and pharmaceutical breakthroughs.
Conclusion#
Through unveiling the often-hidden story of Leptodactylodon ornatus, we unearth essential lessons regarding biodiversity, ecological interconnectedness, and conservation responsibility. We must cherish and protect these delicate, hidden creatures, recognizing their intrinsic value and role they play in maintaining ecological equilibrium.
As stewards of nature and biodiversity, our shared commitment in advocating conservation, education, and ecological preservation will play decisive roles ensuring the enduring survival of species like the Ornate African Forest Frog, guardians quietly living alongside us.