- Exploring <em>Adhaerobufo ceratophrys</em>: The Remarkable Horned Forest Frog
Exploring Adhaerobufo ceratophrys: The Remarkable Horned Forest Frog#
Tucked within the lush, verdant rainforests lies a secretive amphibian, often unnoticed by even the keenest eyes. Meet Adhaerobufo ceratophrys, the horned forest frog, an amphibian as captivating as it is elusive. With its mesmerizing eyes and distinctively pronounced horn-like structures, this species has captivated biologists and nature enthusiasts alike. But despite its striking appearance, little is widely known about its hidden life. Taking a closer look into its world reveals fascinating stories of adaptation, vital ecological roles, and compelling conservation significance.
Taxonomy and Classification#
Scientifically recognized as Adhaerobufo ceratophrys, this amphibian belongs to the family Bufonidae—the true toads. Despite being classified among toads, its stunning, horn-like structures and specialized adaptations have earned it unique interest among herpetologists. The genus Adhaerobufo is relatively small, making its few recognized species subjects of particular biological intrigue. Closely related to other robust-bodied amphibians, the horned forest frog has distinct anatomical and behavioral characteristics setting it apart within its lineage, deepening our understanding of evolutionary pathways among amphibians.
Natural Habitat and Geographical Range#
In the verdant, moisture-soaked understory of subtropical and tropical rainforests, Adhaerobufo ceratophrys finds its home. Predominantly inhabiting the expansive rainforests of South America, particularly regions in Brazil and Paraguay, these frogs prefer damp, shaded forest floors near gentle streams and pools of still water. The dense foliage, leaf litter, and shaded logs provide the perfect environment, offering shelter from potential predators and ideal hunting grounds for their nocturnal activities.
Imagine wandering beneath towering, moss-covered trees, the air thick with humidity, lush greenery surrounding every step—this is where the horned forest frog quietly thrives. Within this pristine microhabitat, the frog performs its daily rituals, relying heavily on moisture and the delicate ecological balance sustained by the rainforest.
Habitat Preferences and Ecosystem Interactions#
The horned forest frog depends on proximity to freshwater sources, both for reproduction and maintenance of their hydration levels. Slow-flowing streams and shallow pools act as vital breeding sites for these amphibians. Thick layers of leaf litter help the frogs remain concealed during daylight, while the moist environment aids their highly permeable skin, a critical adaptation shared by most amphibians.
Physical Characteristics and Adaptations#
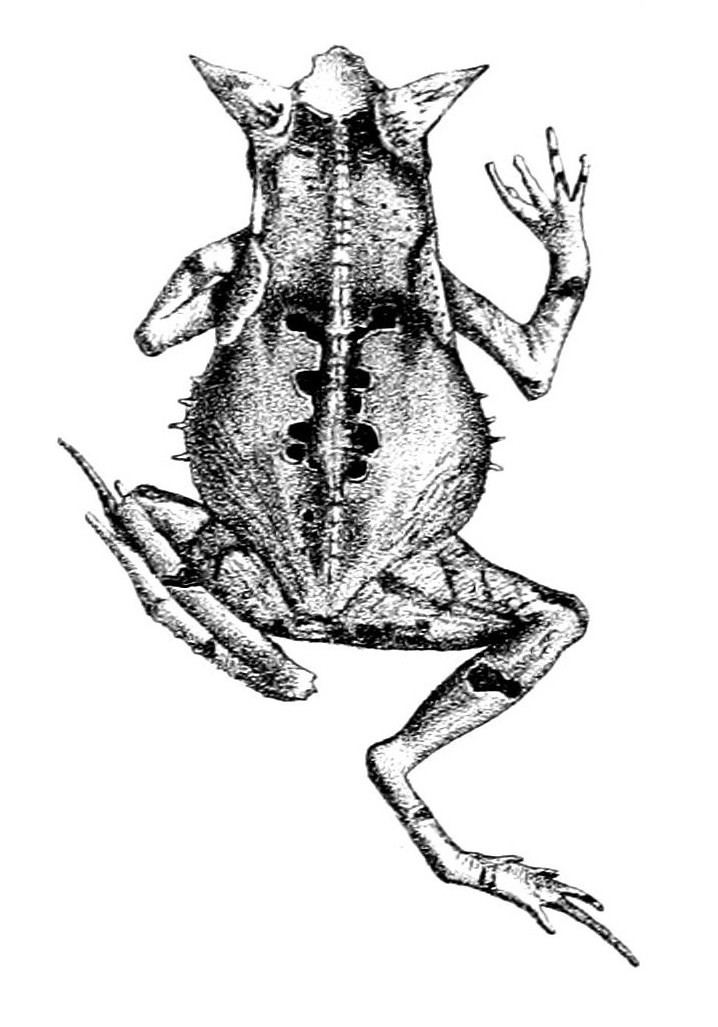
The unique charm of Adhaerobufo ceratophrys becomes immediately evident in its physical characteristics. Typically measuring between 4 to 7 centimeters in length, this robust frog possesses a stocky build that, while appearing harmlessly rotund, hides remarkable musculature suited to a life spent partially concealed beneath leaf litter.
Perhaps most noticeably, the species features prominent horn-like cranial crests above its eyes, giving rise to its common name —the “horned” forest frog. These horns are composed of hardened skin and bone, and though their exact evolutionary function remains a subject of ongoing research, scientists hypothesize they play a critical role in camouflage, intimidation displays, or territorial signaling to other frogs.
Their coloration is yet another marvel of natural engineering. Shades of brown, olive, and tan create intricate patterns resembling fallen leaves, debris, and soil—perfect camouflage helping them evade predators and ambush prey alike. Their skin texture, covered in small bumps and ridges, further enhances this camouflage, enabling near-perfect blending into their surroundings.
Adaptations for Survival#
Besides their notable horns and camouflage abilities, these frogs possess keen sensory organs, specifically adapted for nocturnal hunting. Large forward-facing eyes provide excellent night vision, allowing precise detection of movement from insects, spiders, and other small invertebrates—their primary diet source.
Behavior and Life Cycle#
The horned forest frog spends much of its day quietly hidden beneath piles of leaf litter or nestled among rocks, its cryptic coloration offering protection from watchful eyes. As night approaches and humidity peaks, the frog emerges to hunt. Using a sit-and-wait ambush tactic, it remains perfectly still, relying on its acute eyesight and vibration detection to track and capture insects and invertebrates venturing nearby.
Reproductive Behavior and Tadpole Development#
The rainy season triggers a remarkable transformation in the behavior patterns of these amphibians, ushering in a period of intense breeding activity. Males move towards temporary pools and ponds, where they vocalize with a unique, resonant croaking call. These distinctive calls serve both to establish territories and attract potential mates.
Once mating pairs form, females deposit gelatinous masses of eggs in shallow, stagnant pools, leaves, or even submerged vegetation. Unlike many frog species, Adhaerobufo ceratophrys may insert their eggs into protected niches in the environment, safeguarding against predators and environmental stresses.
Tadpoles hatch and quickly adapt to underwater life, their streamlined bodies and dark coloration suited to life hidden among aquatic vegetation. Over the next few months, these tadpoles grow rapidly, developing limbs as their tails shrink and lungs mature. Emerging at last as miniature replicas of their parents, the newly metamorphosed froglets quickly disperse into the humid forest, beginning their mysterious and secretive terrestrial lives.
Ecological Role and Significance#
Connecting invisibly to broader ecosystems, the horned forest frog plays a significant ecological role. As both predator and prey, this amphibian helps maintain critical balance in forest ecosystems, keeping insect populations in check and providing sustenance for larger predators, such as birds, snakes, and small mammals.
Amphibians, including Adhaerobufo ceratophrys, often serve as essential indictors of environmental health. Their sensitive, permeable skin makes them highly susceptible to pollutants and shifts in their environment. Consequently, their presence—or absence—can indicate the overall vitality and cleanliness of the rainforest habitat, making them invaluable for conservation monitoring efforts.
Threats and Conservation Status#
Despite its remarkable adaptations and secretive lifestyle, the horned forest frog faces growing threats. Habitat loss and fragmentation due to deforestation, logging activities, agricultural expansion, and infrastructure development pose immediate risks. Climate change further complicates matters, altering rainfall patterns, disturbing breeding cycles, and threatening delicate amphibian physiology.
Presently, the Adhaerobufo ceratophrys holds classifications reflecting concerns raised by conservationists. While precise population assessments are ongoing, habitat reduction and degradation clearly place this unique amphibian under growing threat and conservation concern.
Dedicated conservation groups and local environmental authorities have recognized the urgency to protect intact ecosystems. Initiatives promoting habitat conservation, ecological corridors, and sustainable land-use practices are underway, and increased attention is bringing promising steps towards the preservation of both the species and its habitat.
Cultural and Scientific Significance#
Beyond its ecological role, the horned forest frog holds cultural and scientific significance. Indigenous peoples have treasured amphibians as symbols of fertility, renewal, and environmental wisdom, while modern researchers continue to explore these frogs for medical, ecological, and evolutionary insights. While research specifically on Adhaerobufo ceratophrys remains limited compared to better-studied amphibians, ongoing studies promise new discoveries, potentially unveiling genetic attributes or biochemical compounds beneficial to medical or biotechnology fields.
Conclusion#
The horned forest frog, Adhaerobufo ceratophrys, offers an astounding glimpse into the diversity, complexity, and beauty of Earth’s remarkable amphibian life. From its cryptic camouflage to elaborate reproductive behavior, it represents a treasure awaiting discovery, understanding, and most critically, conservation. Each of us can play a role—supporting conservation initiatives, spreading awareness, advocating for sustainable lifestyles, and ensuring that this extraordinary creature flourishes for generations to come. Let our curiosity become stewardship, guiding us toward deeper relationships with the living tapestry that sustains ourselves and the countless unique species with whom we share our shared planet.