- Discovering Ingerophrynus gollum: The Fascinating Saga of the Gollum Toad
- Taxonomy and Classification: Solving the Puzzle of Identity
- Natural Habitat: A Realm Hidden Beneath Leaves
- Physical Characteristics: An Unconventional Beauty
- Behavior and Life Cycle: Unveiling Hidden Habits
- Ecological Role: Guardians of Forest Health
- Threats and Conservation Status: Struggling Against the Changing Times
- Cultural and Scientific Significance: Stories from Forest Lore
- Final Reflections: Championing a Future for the Gollum Toad
Discovering Ingerophrynus gollum: The Fascinating Saga of the Gollum Toad#
Hidden away beneath the damp foliage and tangled roots of Southeast Asia’s dense forests lives an amphibian whose very name conjures images of fantasy and myth—Ingerophrynus gollum. Known affectionately among scientists and nature lovers as the “Gollum Toad,” this elusive amphibian draws its name from a beloved Tolkien character, reflecting its unique appearance and secretive behaviors. Yet, far from fiction, Ingerophrynus gollum brings its own fascinating narrative of adaptation, ecology, and conservation, deserving of its time in the spotlight.
Discovered and described as recently as 2007, I. gollum is a toad that exemplifies the complexities and wonders of tropical biodiversity. While the world often celebrates charismatic animals like tigers, elephants, or pandas, the story of lesser-known creatures such as the Gollum Toad brings our attention to the often-overlooked corners of ecosystems. Their intriguing biology, delicate ecological role, and sensitivity to environmental change make them crucial indicators of habitat health, underscoring the significance of amphibian conservation.
Taxonomy and Classification: Solving the Puzzle of Identity#
Ingerophrynus gollum belongs to the Bufonidae family, one of the largest amphibian families, commonly referred to as “true toads.” The Bufonidae family contains hundreds of species broadly distributed across the globe. Within this family, the genus Ingerophrynus consists of Asian toads characterized by distinct physical and ecological adaptations to tropical forest habitats.
When scientists first described this species in 2007, they chose a name reflecting its unusual appearance. The term “gollum” was deliberately selected due to the animal’s distinctive morphology, reminiscent of J.R.R. Tolkien’s fictional character known for his unique and striking phenotype.
Closely related to Ingerophrynus divergens and Ingerophrynus quadriporcatus, I. gollum shares common ancestry and ecological requirements with its congeners. However, precise molecular studies have confirmed distinct genetic lineages, validating its status as a separate and unique species worthy of careful conservation attention.
Natural Habitat: A Realm Hidden Beneath Leaves#
Finding Ingerophrynus gollum in its natural habitat can be a challenging endeavor. Native to regions including Peninsular Malaysia, Borneo, and parts of Indonesia and Thailand, this enigmatic toad chooses environments judiciously. Primarily occupying lowland to hilly tropical rainforests, the Gollum Toad favors humid, shaded forest floors rich with leaf-litter and decomposing vegetation—an environment teeming with insect prey and providing ample hiding spaces from predators and human disturbance.
The dampness and concealment of its chosen habitat are vital for I. gollum, contributing to skin hydration, fewer predators, and abundant food sources. Tightly linked to pristine, undisturbed ecosystems, the survival of the species is intimately connected to forest conservation and responsible land-use practices. Its cryptic lifestyle necessitates preservation not only of fragmented habitat patches but also crucial forest corridors connecting populations across its distribution.
Beyond dense leaf-litter, these amphibians also frequent the edges of clear-flowing streams and temporary forest pools formed during the rainy season, essential for their breeding cycles. Such breeding sites underscore the critical role intact water systems play in their survival strategies.
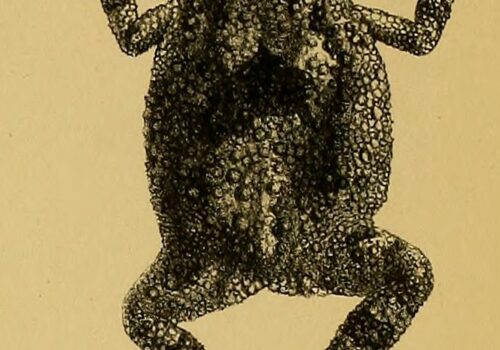
Physical Characteristics: An Unconventional Beauty#
At first glance, the Gollum Toad may not embody the traditional perception of outward amphibian beauty. Yet, through careful observation and appreciation, its peculiar and fascinating form reveals a compelling evolutionary narrative sculpted by millions of years of selective pressures.
Typically small-to-medium-sized amphibians, adults measure between approximately 30 to 50 mm in body length, males often slightly smaller than females. Their coloration varies subtly, exhibiting shades of dark brown, gray, or olive green, shades that perfectly camouflage them among the damp leaves and mossy stones of their rainforest home. Their cryptic colors provide essential concealment from predators, enhancing survival rates significantly.
Adding to their intriguing appearance, Ingerophrynus gollum exhibits characteristic granular skin, notably covered with wart-like glands. These glands secrete mild toxins to deter predators—a potent defense mechanism common among toads, ensuring predators learn quickly to steer clear.
Perhaps most striking are their large eyes, essential for hunting among dense, often dark foliage. These eyes possess vertically-oriented pupils, adept at capturing minimal and fragmented light beneath thick rainforest canopy layers. Collectively, the frog’s intricate blend of color, texture, and form makes it a fascinating subject of evolutionary study and observation, uniquely adapted for quiet existence amidst tropical undergrowth.
Behavior and Life Cycle: Unveiling Hidden Habits#
Feeding Strategies: Masters of Ambush#
The Gollum Toad is an adept predator, feeding primarily on small arthropods including ants, termites, beetles, and various small insects abundant in leaf litter. Rather than active pursuits commonly seen in frogs inhabiting open habitats, I. gollum prefers an ambush strategy, waiting patiently, motionless and concealed, until an unsuspecting invertebrate wanders into striking range. Utilizing their well-developed eyes, they expertly time their rapid tongue-strikes, securing nourishment needed to sustain their relatively hidden lifestyle.
Mating and Reproduction: Rituals Beneath the Canopy#
The reproductive habits of the Gollum Toad reflect deep evolutionary ties with the rainforest ecology. With the arrival of rainy season, males gather near streams and temporary pools, intensifying their calls in an orchestra of trills and whistles echoing gracefully beneath the forest canopy. These choruses are essential; females select mates based on calls’ quality, frequency, and intensity, thus ensuring only strong, healthy genes are perpetuated.
Females lay gelatinous egg masses numbering in the hundreds, anchored subtly to submerged vegetation or beneath rocks. Because rainfall dictates breeding patterns by creating temporary aquatic habitats necessary for eggs and subsequent tadpole development, climate stability is vital for their reproductive success. The tadpoles metamorphose in a matter of weeks, rapidly evolving their aquatic physiology into terrestrial adaptations that enable survival on forest floors, perpetuating the cycle of life.
Ecological Role: Guardians of Forest Health#
Amphibians, generally sensitive to environmental degradation, serve as essential biological indicators. The silent, cryptic lifestyle of I. gollum belies its importance in ecological webs. Acting both as predators—controlling insect populations— and prey—sustaining larger predators, including birds, snakes, and mammals—they significantly contribute to balanced ecosystems.
Through predation of arthropods, Gollum Toads aid in natural pest control mechanisms, indirectly supporting forest health and stability. Conversely, their presence as prey species fosters biodiversity, reflecting interconnectedness across trophic levels.
Threats and Conservation Status: Struggling Against the Changing Times#
Currently classified by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as “Near Threatened,” Ingerophrynus gollum faces several urgent conservation challenges. Foremost among these is habitat destruction due to logging, agriculture, and human expansion. As forests disappear, the critical microhabitats and breeding sites vital for their existence diminish, resulting in fragmented populations and declining numbers.
Additionally, climate change exacerbates pressures on the delicate amphibian lifecycle, altering seasonal rainfall patterns essential for successful breeding. Pollution, pesticide run-off from nearby agricultural lands, and the introduction of exotic competitors or predators threaten the delicate balance needed for these species’ survival.
Cultural and Scientific Significance: Stories from Forest Lore#
The fascinating name and symbolism associated with the Gollum Toad have piqued curiosity and interests beyond scientific circles. While cultural traditions in local indigenous communities often regard amphibians symbolically—depicting aspects of nature’s vitality or fragility—the scientific interest around I. gollum primarily arises from the study of amphibian toxins and ecological indicators. This carefully studied toad exemplifies how meticulous scientific inquiry can illuminate hidden links between ecology, biodiversity, and human survival.
Final Reflections: Championing a Future for the Gollum Toad#
The Gollum Toad embodies the beauty of discovery, hidden worlds, and conservation awareness. Protecting Ingerophrynus gollum requires dedicated conservation stewardship, robust habitat preservation, and heightened awareness among the general public. By supporting forest conservation initiatives, educating ourselves about amphibian ecology, and advocating sustainable practices, we all can ensure the continued survival of this intriguing species. Let us value and preserve such creatures—not as curious oddities but as invaluable treasures reflecting biodiversity’s richness.