- Atelopus ignescens: Rediscovering Ecuador's Legendary Jambato Harlequin Frog
- Taxonomy and Classification of the Jambato Harlequin Frog
- A Naturalist's Paradise: Geographic Range and Habitat Preferences
- A Splash of Vibrancy: Physical Characteristics of <em>Atelopus ignescens</em>
- The Secret Life of the Jambato Harlequin Frog: Behaviors and Reproduction
- The Role of <em>Atelopus ignescens</em> in the Andean Ecosystem
- Surviving Against the Odds: Conservation Status and Threats
- The Cultural and Scientific Legacy of the Jambato Harlequin Frog
- Hope for the Jambato Harlequin Frog and Our Shared Responsibility
Atelopus ignescens: Rediscovering Ecuador’s Legendary Jambato Harlequin Frog#
Hidden among Ecuador’s mist-laden Andes mountains, concealed amidst lush cloud forests and rushing highland streams, is a creature whose mere existence embodies hope, resilience, and natural wonder. Meet Atelopus ignescens, known commonly and affectionately as the Jambato Harlequin Frog. Once considered extinct for nearly three decades, this exquisitely colored amphibian has not only captured the imagination of conservationists around the globe but stands today as a powerful symbol of nature’s perseverance and our shared responsibility for the planet’s future.
For generations, the vibrant coloration and unique behaviors of this species fascinated local communities, scientists, and wildlife enthusiasts alike—until troubling silence descended upon its tiny, amphibian world. Fortunately, the rediscovery of the Jambato Harlequin Frog is more than a heartwarming conservation tale; it’s a bold reminder of the intricate connections between wildlife, ecosystems, and human intervention.
Taxonomy and Classification of the Jambato Harlequin Frog#
Atelopus ignescens belongs to the Bufonidae family, commonly known as true toads. Despite this familial affiliation, this captivating amphibian is lythe and slender, distinct in appearance and behavior from the more familiar, robust global image of a toad. Within its diverse genus Atelopus, ignescens shares kinship with an extraordinary array of harlequin frogs, many of which are known for their radiant coloration patterns and powerful skin toxins.
Harlequin frogs encompass a range of vibrant species scattered throughout Central and South American landscapes, each highly adapted to their unique habitats. The genus represents an evolutionary tapestry that converges in Ecuador’s Andes mountains, with A. ignescens playing a fascinating ecological and evolutionary role in this unique community.
A Naturalist’s Paradise: Geographic Range and Habitat Preferences#
The mysterious cloud forests of Ecuador’s Andes are the exclusive domain of Atelopus ignescens. Historically, its range extended predominantly through central and northern Ecuador’s high-elevation habitats, specifically on the western slopes between 2,600 and 4,200 meters above sea level. These habitats are uniquely suited to this exquisite amphibian, characterized by cool, consistently moist conditions punctuated by fast-moving streams, rocky creeks, abundant moss coverage, and dense montane vegetation.
Within these environments, subtle microhabitats form intricate ecological niches. Pebbled riverbanks and humid, rocky outcrops provide ideal hunting grounds and safe shelters for the frogs. Unlike many amphibians that populate lower-altitude rainforests, this harlequin frog fully embraces the cooler temperatures, high moisture content, and consistent cloud cover, thriving uniquely where other amphibian species might struggle.
Imagine a morning in this compelling Andean landscape: the mist slowly dissipates, revealing countless shades of green woven into a glistening tapestry of foliage. Beneath the forest canopy, tiny threads of water trickle down toward rushing streams, nurturing delicate communities of mosses and ferns. Here, upon a wet stone, the brilliant flash of orange and black from a perching frog’s leg hints unmistakably at the presence of Atelopus ignescens, poised diligently, constantly vigilant in its thriving yet demanding home.
A Splash of Vibrancy: Physical Characteristics of Atelopus ignescens#
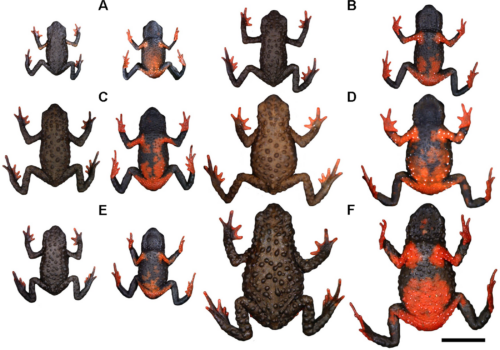
The Jambato Harlequin Frog’s dazzling beauty has long fascinated those fortunate enough to encounter it. Adult frogs are relatively small, rarely exceeding 4 centimeters in length. Their slender, graceful form, with elongated limbs and delicate digits, belies impressive agility and remarkable adaptations for navigating the slippery rocks beside mountain streams.
The most recognizable characteristic has always been its extraordinary coloration—a vibrant palette of intense, fiery orange or bright red, sharply contrasted by irregular black patterns cascading across its back and sides. This distinctive color scheme echoes the wandering patterns of molten lava against volcanic rock, a possible inspiration behind local traditions and vibrant folklore.
Another stark adaptation is the frog’s smooth skin, permeated with potent toxins—defensive compounds designed to deter predators. These toxins are a powerful evolutionary tool, rendering their striking and vivid colors a classic example of aposematic—or warning—coloration. Predators quickly learn that such flamboyance in the animal kingdom often signals danger, allowing the frogs heightened security as they forage boldly in their habitats.
The Secret Life of the Jambato Harlequin Frog: Behaviors and Reproduction#
Hunting, Feeding, and Daily Routines#
The Jambato Harlequin Frog hunts predominantly insects, targeting tiny arthropods abundant along riverbanks and throughout humid undergrowth. During the day, adults can often be found perched visibly amid wet vegetation or poised on exposed rocks, waiting patiently for unsuspecting prey to venture within striking range.
While visually active, Atelopus ignescens also relies on finely tuned sensory perception, detecting subtle vibrations and minute movements within their environment. Their long, sticky tongue darts out swiftly to snatch prey, a remarkable evolutionary tool that ensures survival in the densely vegetated, moisture-rich ecosystem they inhabit.
Mating Rituals and Amphibian Romance#
The breeding season introduces fascinating changes to these otherwise solitary creatures. Typically triggered by environmental cues—rainfall patterns and moisture levels—male frogs congregate along streams, showcasing their physical vigor and territorial dominance through unmistakable visual and acoustic displays. Gentle vibrating calls permeate the forest, facilitating interaction among potential mates.
The females, drawn by these delicate serenades, select suitable partners and lay clusters of gelatinous eggs attached firmly beneath submerged rocks or plants, safely hidden from predators. After fertilization, tiny tadpoles emerge, adapted with suction-like mouths to hold tightly against the current. These tadpoles grow within their aquatic nurseries, grazing diligently on algae, eventually transforming into miniature copies of their iconic parents.
The Role of Atelopus ignescens in the Andean Ecosystem#
In this delicate and diverse ecosystem, the Jambato Harlequin Frog fulfills crucial ecological functions. As a dietary generalist, it effectively controls insect populations, maintaining balance within the multifaceted food web of cloud forests. Simultaneously, by serving as prey for snakes, birds, and mammals, it contributes substantially to nutrient cycling and overall biodiversity.
Additionally, like many specialized amphibians, Atelopus ignescens serves as a sentinel species. Its sensitivity to environmental changes such as water pollution, habitat destruction, and climate shifts makes the frog a reliable indicator of ecosystem health. Their well-being helps scientists and conservationists gauge broader ecological integrity, providing vital information about the overall impact of human activities and natural events.
Surviving Against the Odds: Conservation Status and Threats#
Without a doubt, the story of Atelopus ignescens is shadowed by dramatic population declines attributed largely to habitat loss, climate change, and—most significantly—the devastating fungal pathogen chytridiomycosis. For decades, conservationists feared its total extinction, with the species classified as Critically Endangered or possibly Extinct in the Wild according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Remarkably, recent rediscoveries of isolated living populations have rejuvenated hope and launched rigorous conservation efforts. Robust captive breeding and reintroduction programs coordinated by international organizations, Ecuadorian government agencies, and passionate local conservationists are now underway, providing promising pathways toward full ecological revival.
The Cultural and Scientific Legacy of the Jambato Harlequin Frog#
Culturally, local Ecuadorian communities have long admired the unique visual aesthetics, associating it with legends about volcanic energies, fire symbols, and mystical beliefs. Scientifically, the frog’s extraordinary chemical makeup has inspired studies into natural toxins, potential medical applications, and ecosystem health indicators, reaffirming the profound scientific value of biodiversity.
Hope for the Jambato Harlequin Frog and Our Shared Responsibility#
The comforting rediscovery of Atelopus ignescens invites deeper reflection and broader commitments. We must embrace our collective responsibility to support conservation efforts and protect biodiversity for generations to come. By learning, sharing, and supporting wildlife preservation initiatives, we can ensure future generations experience the same awe, wonder, and inspiration stirred by the mesmerizing beauty of Ecuador’s legendary Jambato Harlequin Frog.